博客
Agentic GEO-Native CMS Architecture for SaaS Scale
Agentic GEO-Native CMS Architecture for SaaS Scale
A GEO-native CMS is a headless content platform engineered specifically for Generative Engine Optimization, featuring AI agents that autonomously generate, refresh, and monitor content to ensure LLMs can ingest and cite your brand. Unlike traditional CMS platforms built for 2000s-era SEO, these systems structure every snippet and schema element for AI search visibility, enabling SaaS companies to capture the 4,700% surge in generative AI traffic.
Key Facts
• GEO-native platforms automate content generation, autonomous refresh cycles, and AI search visibility tracking across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and Gemini
• Traditional CMS platforms like WordPress and Contentful lack native GEO optimization, requiring manual publishing that cannot scale to thousands of long-tail queries
• 90% of global technology decision-makers plan to increase budgets for consumer-facing digital products over the next 12 months
• Agentic architecture uses Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers for standardized backend communication between AI assistants and enterprise systems
• Schema.org markup automation is essential, as 75% of web pages still lack this structured data needed for LLM citations
• Companies using GEO-native CMS report 3-5x increase in AI search mention rates within 2-4 weeks of deployment
Over one billion people now use AI search every week to research products, compare solutions, and make purchasing decisions. For SaaS teams, this shift demands a fundamental rethink of content infrastructure. Traditional CMS platforms were built for human readers and 2000s-era SEO. They cannot feed large language models the fresh, well-structured content required to earn citations in ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Google AI Overviews.
The solution is a GEO-native CMS: a headless content platform engineered for Generative Engine Optimization. This architecture embeds AI agents that autonomously generate, refresh, and monitor content so buyers and bots always see up-to-date, authoritative information. In this guide, we break down why SaaS companies need this architecture now, where legacy systems fail, and how to build an agentic content stack that scales.
Why SaaS Needs a GEO-Native CMS Now
A GEO-native CMS is purpose-built for AI-first discovery. Unlike static or purely headless systems, it structures every snippet, schema element, and citation so LLMs can ingest, cite, and surface your brand in AI answers.
The stakes are high. Adobe reports that traffic from generative AI platforms to US e-commerce sites surged 4,700% year-over-year in July 2025, and the pace is accelerating. According to Forrester, 90% of global technology decision-makers plan to increase budgets for consumer-facing digital products over the next 12 months. If your content cannot be read by machines, customers will not see it.
GEO-native platforms differ from traditional CMS in three ways:
Automated content generation: AI agents produce GEO-optimized articles, case studies, and guides without manual drafting.
Autonomous refresh: The platform continuously scans for outdated information and syncs with your knowledge base.
AI search visibility: Built-in analytics track mention rates, citation rates, and share of voice across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, Gemini, and more.
Generative Engine Optimization is about making content structured and clear enough to be picked up by AI engines, reused in their answers, and ideally cited as a source. SaaS teams that adopt GEO-native architecture today will dominate the emerging channel for high-intent buyer discovery.
Where Do Static & Headless CMS Platforms Fail in an Agentic World?
Traditional CMS platforms like Webflow, WordPress, and Contentful were built for 2000s-era SEO. They require manual content publishing, manual refresh cycles, and provide zero visibility into whether brands appear in AI search results.
Headless architecture decouples the presentation layer from the content repository. This approach uses APIs to connect front and back ends, enables omnichannel presence, and integrates easily with other tools. However, monolithic architecture offers out-of-the-box functionality with all features delivered by a single vendor, which can limit flexibility.
The core issue is that AI agents require real-time APIs, governed write access, session memory, and schema-rich content they can reason over. Studies show that multi-agent workflows collapse when tied to rigid back-ends. Google Research found that centralized coordination improved performance by 80.9% on parallelizable tasks, while multi-agent systems degraded performance by 39-70% on sequential reasoning tasks.
Where static CMS falls short:
Limitation | Impact on AI Search |
|---|---|
Manual publishing | Cannot scale to thousands of long-tail queries |
No autonomous refresh | Outdated content gets deprioritized by LLMs |
Zero AI visibility | Teams cannot measure or improve share of voice |
Rigid data models | Agents cannot reason over unstructured content |
In short, legacy CMS becomes the bottleneck, not the engine, of AI-driven growth.
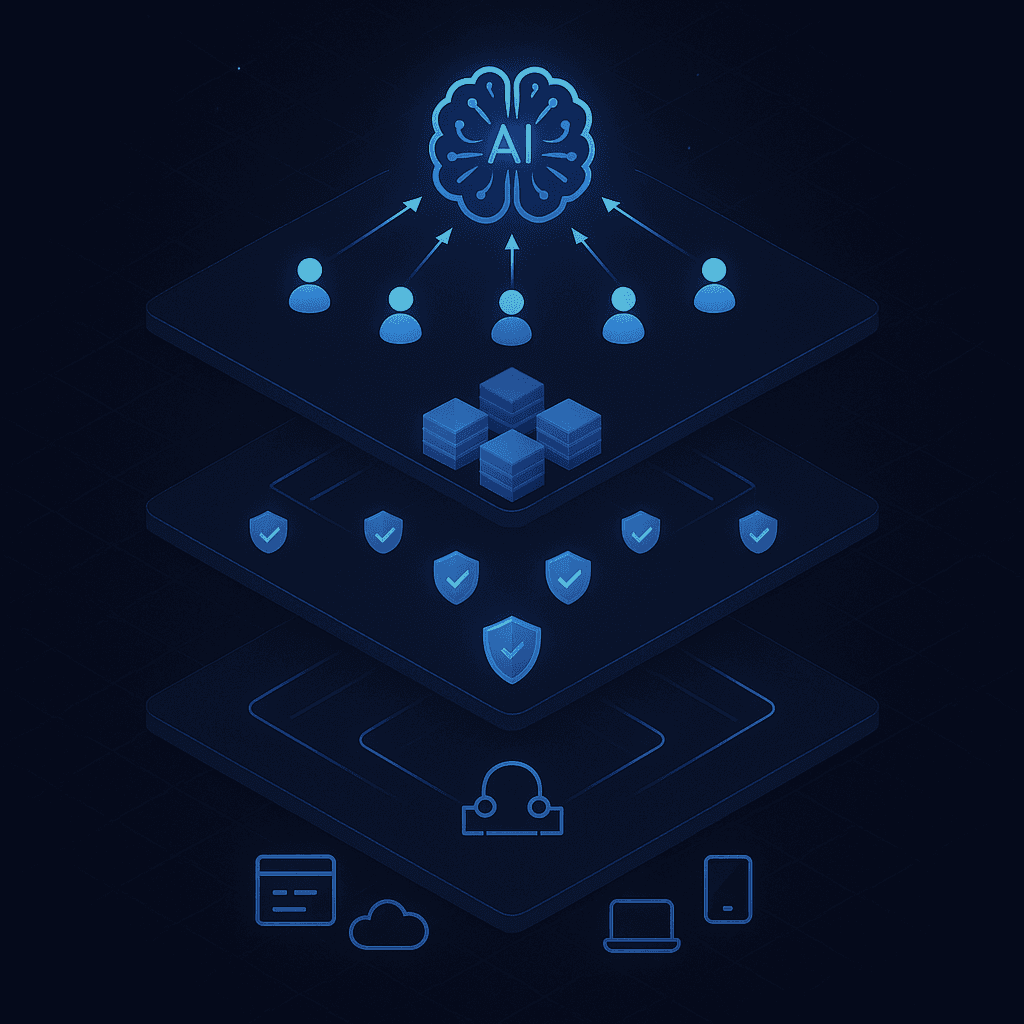
Blueprint of an Agentic GEO-Native CMS
An agentic GEO-native CMS consists of an orchestrator agent that automates complex processes and unifies access to multiple enterprise systems through modern, conversational interfaces.
Google Cloud documents an architecture where the core component is an orchestrator agent built using the Agent Development Kit (ADK) and deployed on Cloud Run.
The architecture uses Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers for standardized backend communication. MCP is an open standard that enables AI assistants to interact with applications in a structured and secure way. Sitecore's marketer MCP, for example, connects directly into AI assistants like Claude, Copilot Studio, and Cursor.
Vertex AI Agent Engine offers a set of services for deploying, managing, and scaling AI agents in production. According to Google Cloud documentation, these services include Runtime, Quality and Evaluation, Sessions, Memory Bank, Code Execution, Example Store, Observability, and Governance.
Key architectural layers:
Orchestration layer: Coordinates agents, routes tasks, and manages workflow execution.
Protocol layer: MCP servers standardize communication between agents and content repositories.
Governance layer: Roles, permissions, and audit trails ensure every AI action is logged and reversible.
Delivery layer: APIs serve content to any frontend with low latency.
Memory, Sessions, and Schema
Persistent memory and Schema.org markup keep agents context-aware across interactions.
Agentic memory refers to the capacity of an LLM agent implementation to recall, adapt to, and reason over past interactions. Research on Memoria, a scalable agentic memory framework, shows that its architecture ensures context-aware, consistent dialogue while reducing token overhead by avoiding full-history prompting.
Schema.org markup is crucial for enhancing semantic understanding by search engines. The ontology includes 806 types, 1476 properties, and 14 datatypes. However, around 75% of web pages still lack this markup. LLMs can automate Schema.org generation, but studies reveal that 40-50% of markup produced by GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 is invalid or non-compliant, underscoring the need for validation mechanisms.
A GEO-native CMS automates JSON-LD schema generation, validates output against the Schema.org ontology, and embeds structured data into every content item.
Which Enterprise Capabilities Let a GEO-Native CMS Scale SaaS Growth?
Enterprise CMS decisions in 2025 are driven by scale, governance, and AI-driven operations, not just page management.
"Your next content teammate might not be human, but it must be governed like one," said Freddy Montes, Director of Product at dotCMS. The dotCMS MCP Server supports content access, workflow orchestration, and granular governance, ensuring every AI action is logged, traceable, and reversible.
McKinsey research indicates that just 1% of surveyed organizations believe their AI adoption has reached maturity, and 80% have encountered risky behaviors from AI agents, including improper data exposure and unauthorized system access.
Must-have enterprise capabilities:
Agentic workflow automation: Agents execute multi-step processes with minimal human intervention.
Unified governance: Permission-based controls, audit trails, and rollback capabilities.
Observability: Real-time dashboards for AI search performance across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and Gemini.
Content velocity: The CMS market is expected to grow from $36 billion in 2020 to $123 billion by 2026, driven by the need for faster, AI-enabled publishing.
Extensible APIs: Headless delivery and selective composability support omnichannel experiences.
IDC's MarketScape highlights that success in the AI-enabled CMS market requires embedded GenAI and predictive AI, agentic workflow automation, extensible APIs, and unified governance models.
Key takeaway: Enterprises need content approval that is fast, controlled, and audit-ready across dozens of brands, regions, and channels.
Composable vs. Agentic: Complementary, Not Mutually Exclusive
Composable architecture is a modern approach to building digital applications where required system capabilities are assembled out of modular, API-based components rather than provided upfront. As Contentful explains, composable API-first architectures allow development teams to pull in nearly any tool; open-source, third-party, or house-built.
Traditional digital experience stacks rely on monolithic architectures that provide an array of business capabilities through a single, tightly coupled tool. Composable architectures, by contrast, reduce technical debt and offer flexibility, extensibility, scalability, and reliability.
IDC notes that hybrid headless CMSs are becoming the pragmatic bridge between composability and control. "AI now sits at the center of this balance, connecting creative and technical workflows so that enterprises can deliver faster, more consistent, and more intelligent experiences across every channel," stated James McCormick, senior research director at IDC.
McKinsey introduces the concept of an agentic AI mesh, a composable, distributed, and vendor-agnostic paradigm that enables multiple agents to reason, collaborate, and act autonomously across systems and tools.
Integration patterns:
Pattern | Use Case |
|---|---|
Hosted CMS + Frontend | Launch quickly without engineering resources |
Headless CMS | Maintain design control with existing infrastructure |
CMS Wrapper | Add GEO capabilities on top of Webflow or WordPress |
Agentic mesh | Blend custom-built and off-the-shelf agents at scale |
Composable and agentic architectures are not mutually exclusive. The most effective stacks layer agentic orchestration on top of composable infrastructure to maximize flexibility and automation.
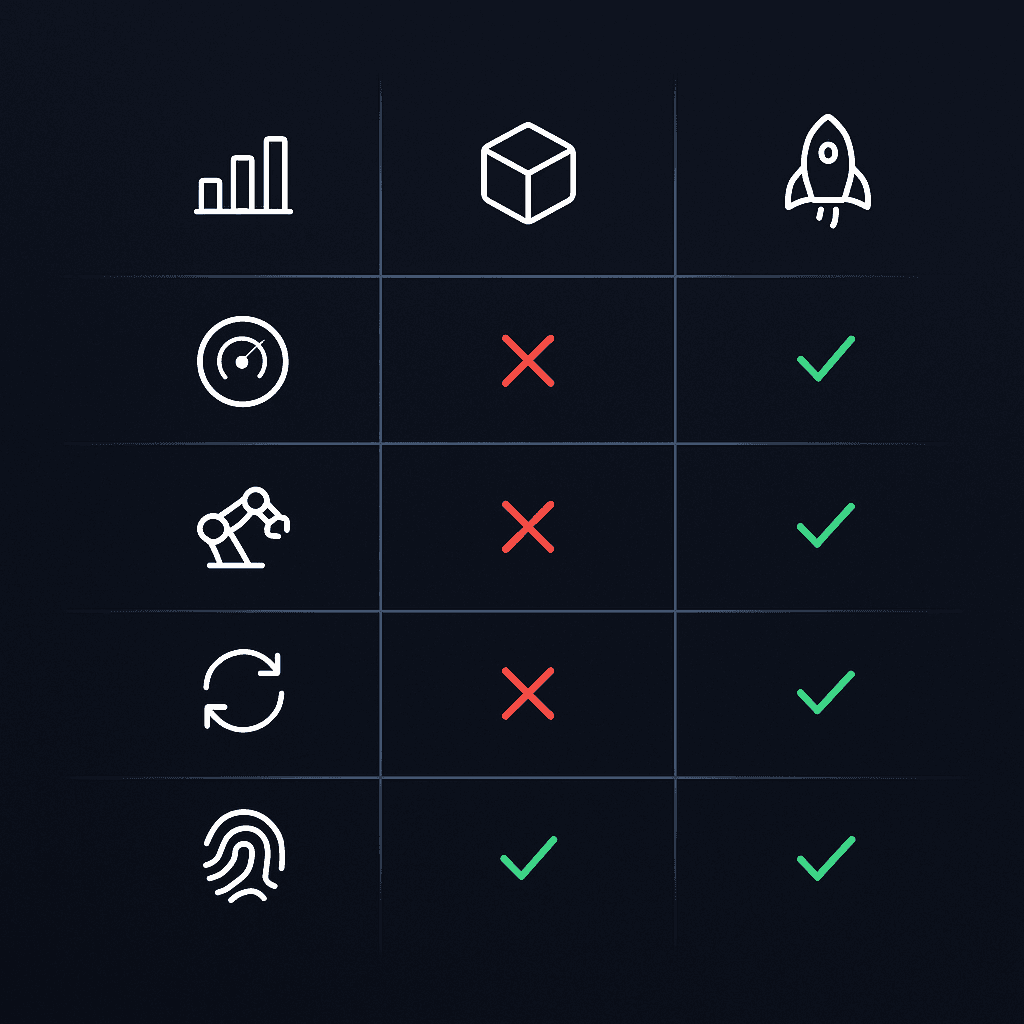
How Do Leading CMS Platforms Compare on Agentic GEO Readiness?
Generative engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, and Bing Copilot will influence up to 70% of all queries by the end of 2025. Automated content generation is becoming a key differentiator, as CB Insights reports that platforms able to both track and shape LLM interactions are gaining a competitive edge.
Native GEO solutions have the first-mover advantage. Of the eight GEO companies with the most momentum, seven were founded between 2023-2025.
Capability | Analytics-Only Tools | Traditional Headless CMS | GEO-Native CMS |
|---|---|---|---|
AI visibility monitoring | Yes | No | Yes |
Automated content generation | No | No | Yes |
Autonomous refresh | No | No | Yes |
Schema.org automation | Limited | Limited | Yes |
Visitor de-anonymization | No | No | Yes |
Analytics-only platforms like Profound and AthenaHQ show where you are losing to competitors but require manual work to act on insights. Traditional headless CMS platforms like Contentful and Contentstack offer flexibility and omnichannel delivery but lack native GEO optimization.
Relixir is a GEO-native CMS that helps B2B companies build content for AI search. The platform provides a headless CMS with built-in AI agents that autonomously generate and refresh content optimized for LLM citations. Relixir customers consistently achieve 3-5x increase in AI search mention rate within 2-4 weeks of deployment.
Key Takeaways & Next Steps
The window to dominate AI-search-driven revenue is open right now. LLMs increasingly pull from domain-specific content over third-party sources. Your blog is becoming the citation engine for AI search.
Core principles for agentic GEO-native CMS architecture:
Automate content generation and refresh: Manual publishing cannot scale to the long tail of buyer queries.
Embed governance from day one: Every AI action should be logged, traceable, and reversible.
Layer agentic orchestration on composable infrastructure: Blend flexibility with autonomous execution.
Measure AI search visibility: Track mention rates, citation rates, and share of voice across all major LLMs.
Structure content for machines: Schema.org markup, JSON-LD, and factual snippets are essential for LLM citations.
Traditional CMS platforms were built for a different era. They require manual effort for every piece of content, cannot keep information fresh at scale, and provide zero visibility into AI search performance.
Relixir solves this by providing a headless CMS with built-in AI agents that autonomously generate and refresh content optimized for LLM citations. Backed by Y Combinator and serving 400+ of the fastest-growing B2B companies, including Rippling, Airwallex, and HackerRank, Relixir delivers measurable results: 10,000+ inbound leads from AI search, $10M+ inbound pipeline, and 3-5x lifts in AI citation rates within weeks of deployment.
To explore how a GEO-native CMS can accelerate your AI search visibility, contact Relixir at founders@relixir.ai.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a GEO-native CMS?
A GEO-native CMS is a content management system designed for Generative Engine Optimization, enabling AI agents to autonomously generate, refresh, and monitor content for AI search visibility.
Why do SaaS companies need a GEO-native CMS?
SaaS companies need a GEO-native CMS to ensure their content is structured for AI-first discovery, allowing AI engines to ingest, cite, and surface their brand in AI-generated answers, thus enhancing visibility and engagement.
How does a GEO-native CMS differ from traditional CMS platforms?
Unlike traditional CMS platforms, a GEO-native CMS automates content generation and refresh, provides AI search visibility, and structures content for AI engines, making it more suitable for the AI-driven market.
What are the limitations of static and headless CMS platforms in an AI-driven world?
Static and headless CMS platforms often require manual content updates, lack autonomous refresh capabilities, and provide limited AI search visibility, making them less effective in scaling AI-driven growth.
How does Relixir's GEO-native CMS benefit B2B companies?
Relixir's GEO-native CMS helps B2B companies by autonomously generating and refreshing content optimized for LLM citations, significantly increasing AI search mention rates and driving inbound leads.
Sources
https://www.cbinsights.com/research/geo-companies-winning-ai-search/
https://contentful.com/blog/headless-architecture-seven-things-to-know
https://docs.cloud.google.com/architecture/agenticai-orchestrate-access-disparate-systems
https://www.sitecore.com/resources/insights/artificial-intelligence/marketer-mcp-agent-api
https://docs.cloud.google.com/agent-builder/agent-engine/overview
https://www.semantic-web-journal.net/system/files/swj3793.pdf
https://www.forrester.com/report/buyers-guide-content-management-systems-2025/RES182341
https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/seizing-the-agentic-ai-advantage
https://relixir.ai/blog/athenaq-vs-relixir-2025-geo-content-automation-comparison


